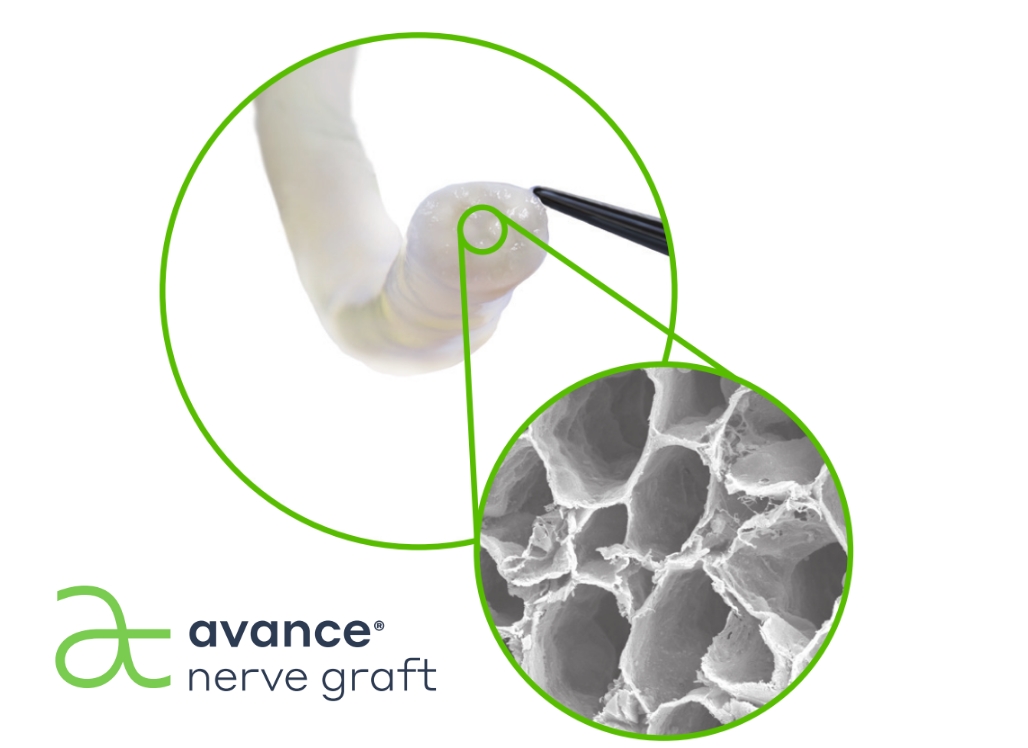
for motor and sensory nerve repair
allograft is a new standard of care
Data continues to confirm allograft nerve repair efficacy and economics are comparable to autograft for motor and sensory nerves across gaps up to 70 mm.
allograft outcomes are comparable to autograft1

evidence
1,550+ nerve repairs across 35 studies
Meta-analysis examining the most comprehensive clinical evidence to date

key takeaway
Allograft demonstrates comparable outcomes to autograft in both mixed-motor and sensory nerve gap repair

more findings
No significant differences between allograft and autograft, holding true across:
• Motor and sensory
• >5 to ≤30 mm gaps
• 30 to ≤70 mm gaps
allograft: a cost-comparable alternative to autograft2

evidence
1,360+ peripheral nerve graft repairs
Cross-sectional study of procedure costs for allograft and autograft repairs

key takeaway
Allograft and autograft procedure costs are not statistically different
- Inpatient: $24,733 for allograft, $23,694 for autograft
- Outpatient: $9,874 for allograft, $9,621 for autograft

more findings
Allograft nerve repair saves OR time compared to autograft
- Inpatient: Saves 13.7 minutes
- Outpatient: Saves 40.5 minutes


… allograft nerve reconstruction is an effective and cost comparable treatment to autograft nerve reconstruction that avoids the burden, risk and long-term complications from harvesting a healthy nerve.”
— JOSEPH F. STYRON, MD, PhD
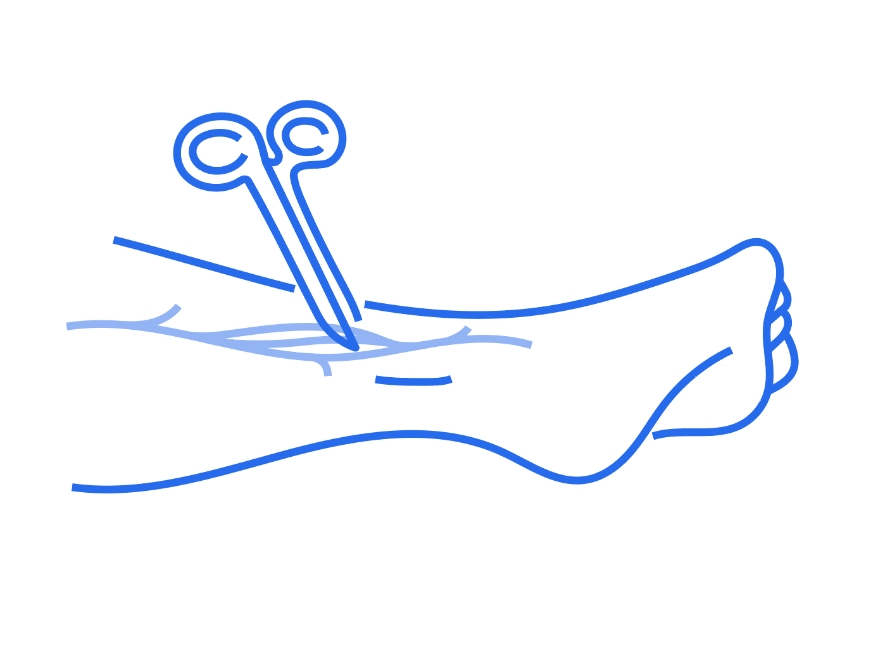
allograft eliminates the risk of complications at a second surgical site
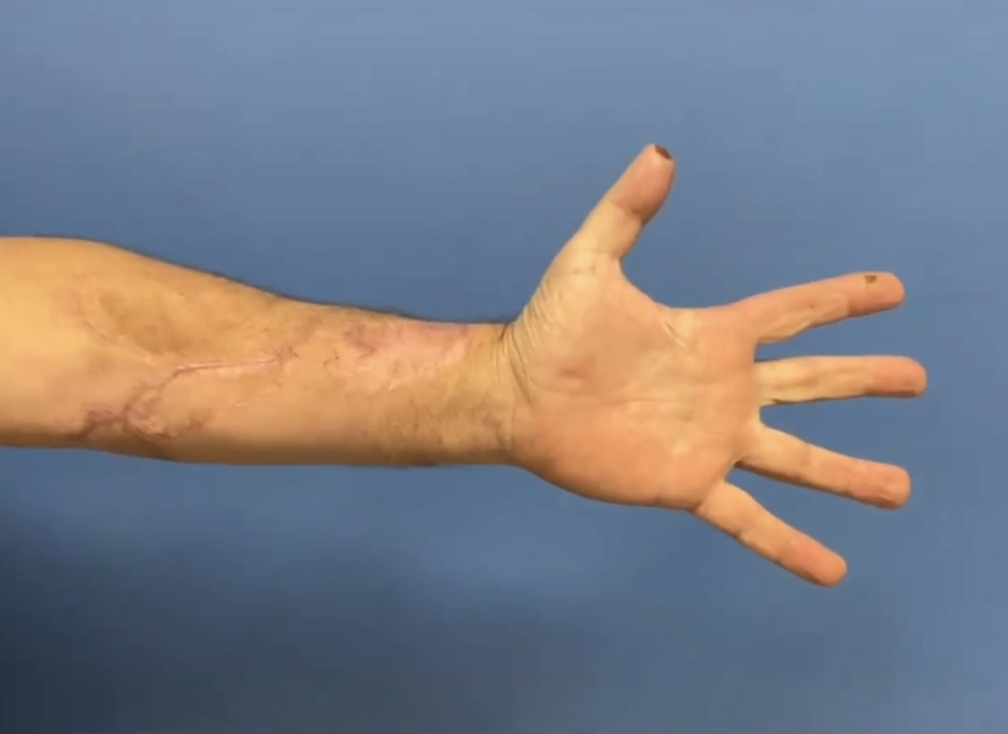
The probability of autograft donor site complication is high with symptoms like chronic pain (25.6%), functional impairment (10%), cold sensitivity (22.2%), sensory loss (87.2%).3
When compared to autograft, allograft is established as a suitable and often preferred method of nerve reconstruction with comparable outcomes.*1
*Results of a survey of 461 hand surgeons with their method for repairing a 2 cm digital nerve gap
PlayAutograft nerve repair for gaps less than 70 mm requires an additional surgical procedure for the patient and brings the risk of secondary site comorbidities that can disrupt patients’ quality of life long after surgery.
secondary site comorbidities3
Patients who received an autograft nerve repair required a secondary site incision, leading to:
- 87.2% sensory loss
- 25.6% rate of pain
- 22.2% cold sensitivity
- 10.0% functional impairment
Allograft nerve repair does not require an additional procedure, which decreases the time spent in the OR and cuts down on overall costs.2 Avance® Nerve Graft is the only off-the-shelf biologically active processed human nerve allograft available in a variety of lengths and diameters for intraoperative versatility.
See the clinical evidence
PlayThe autograft did have chronic implications for my quality of life that maybe an allograft wouldn’t have. There wasn’t an allograft option presented at all [to me].”
– DALTON, AUTOGRAFT PATIENT
The Avance Method® is Axogen’s proprietary methodology for ensuring quality of the Avance Nerve Graft, including testing to ensure identity, purity and safety.
learn more 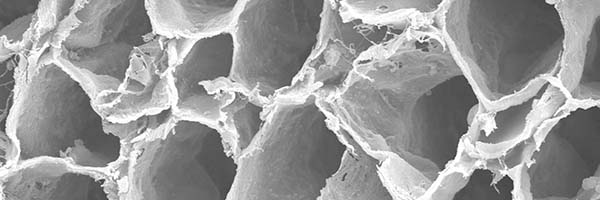
preserved architecture
Preserves the delicate 3D macro- and micro-architecture of native nerve, which provides structural support for the regenerating axons.
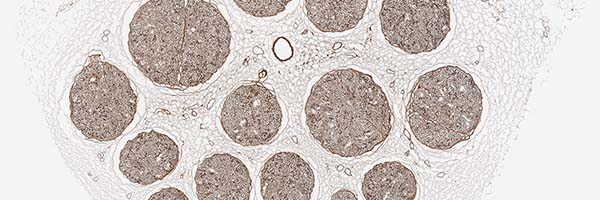
bioactive laminin
Enzyme treated to inactivate the inhibitory aspects of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) exposing laminin, which is known to promote nerve regeneration.4,5
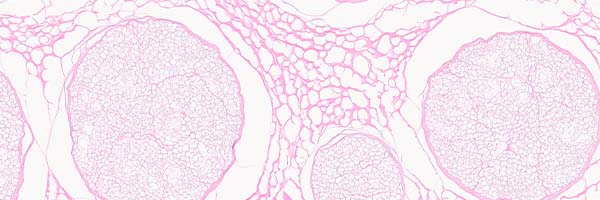
quality assays
Proprietary testing to ensure identity, purity and safety.


This study takes the established fact that allograft is a suitable and often preferred method of nerve reconstruction and expands upon its desirability by showing it is also a cost neutral alternative to autograft. Despite having a higher implant cost, the study shows that allograft nerve repairs have statistically comparable procedure costs due to the offset of OR, room and board and other direct costs associated with an autograft nerve harvest and a secondary surgical site.
— RYAN ENDRESS, MD
There’s only a short form between you and our nerve product team who can help you get more information about our nerve repair solutions.
We’re committed to providing resources and experienced coding assistance to support providers in securing reimbursement
references
- Lans J, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of nerve gap repair: comparative effectiveness of allografts, autografts, and conduits. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2023 May 1;151(5):814e-827e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000010088. Epub 2022 Dec 26.
- Raizman NM, et al. Procedure costs of peripheral nerve graft reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2023;11(4):e4908. Published 2023 Apr 10. doi:10.1097/GOX.0000000000004908
- Bamba R, et al. Donor site morbidity after sural nerve grafting: A systematic review. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2021;74(11):3055-3060. doi:10.1016/j.bjps.2021.03.096
- Plantman S, et al. Integrin-laminin interactions controlling neurite outgrowth from adult DRG neurons in vitro. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008;39(1):50-62. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2008.05.015
- Zuo J, et al. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan with neurite-inhibiting activity is up-regulated following peripheral nerve injury. J Neurobiol. 1998;34(1):41-54.